This document mainly focuses on the overseas expansion of Chinese innovative drugs and the situation of Thermo Fisher Scientific in pharmaceutical services. In simple terms, the main contents are as follows:
1. Trends and Models of Chinese Innovative Drugs Going Global
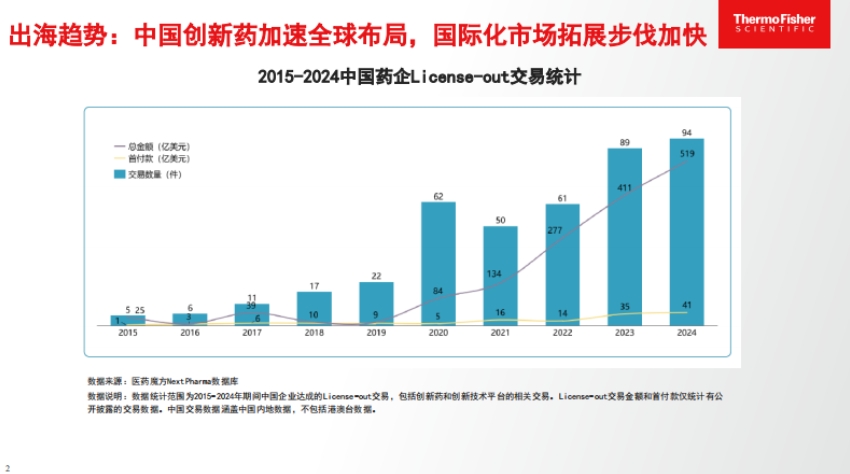
- Faster overseas expansion: From 2015 to 2024, Chinese pharmaceutical companies have engaged in more License-out deals, with both the amount of money and the number of transactions increasing, indicating that Chinese innovative drugs are accelerating their global presence.
- Diverse overseas models: In the early days, most were License-out, meaning only the product rights were sold. There is also independent overseas expansion, where companies build their own commercialization teams and lay out global supply chains; the NewCo model, which brings in international capital to jointly conduct R&D, clinical trials, and commercialization; and mergers and acquisitions, where companies are acquired by multinational pharmaceutical firms, thereby gaining access to international channels and resources.
- Choosing the model based on the company's situation: Companies with strong cash flow and mature pipelines can build their own teams and cooperate to develop global capabilities; those with tight cash flow but strong technology can use License-out to recoup some funds while retaining some regional rights; companies with only early-stage pipelines and unique technologies can use the NewCo model to attract investment; those with good late-stage pipelines and matching technology platforms but limited resources can seek acquisition opportunities.
2. Challenges and Solutions for Independent Overseas Expansion
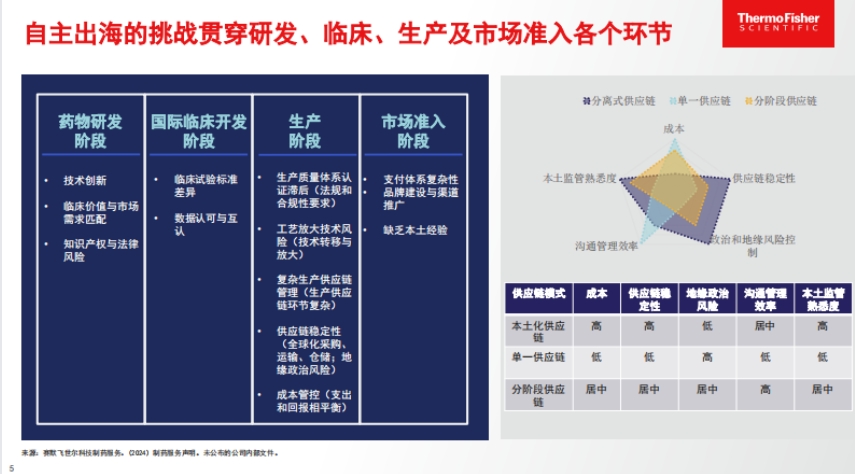
- Challenges faced: Independent overseas expansion faces difficulties in R&D, clinical development, manufacturing, and market access. For example, R&D must align technological innovation with market demand; international clinical development faces differences in standards and data recognition; manufacturing requires quality system certification and handling complex supply chains; market access must deal with complicated payment systems and brand promotion issues.
- Overseas manufacturing risks and countermeasures: Overseas manufacturing involves technical risks, such as technology transfer, production capacity, and quality systems; management risks, as managing remote sites is not easy; and distribution risks, with challenges in transportation, warehousing, and release standards. Patheon, a subsidiary of Thermo Fisher, offers solutions, such as a global technical team and unified quality system for technology; a global transparent communication network for management; and integrated services to help with customs and regulatory issues for distribution.
3. Trends in Biopharmaceutical Manufacturing and Equipment Selection
- Trends: Nowadays, molecular drugs in clinical development require medium-scale production capacity. Traditional large stainless steel bioreactors are less suitable due to high investment, inflexibility, and high contamination risk. Process intensification has boosted the capacity of medium-sized single-use bioreactors, making them a more economical and efficient choice.
- Advantages of 5,000L single-use bioreactors: They can flexibly adjust production capacity, allowing for small-scale production in the early stage and scale-up when demand increases later. Compared to large stainless steel bioreactors, they are lower cost, more reliable, more flexible, and more sustainable, meeting production needs from clinical to commercial stages.
4. Thermo Fisher Scientific's Pharmaceutical Services
- Comprehensive service offerings: They provide pharmaceutical contract development and manufacturing (CDMO) services, covering small molecules, large molecules, clinical trials, and advanced therapies. They also assist with commercial manufacturing, packaging, technology transfer, and support for drug CMC strategy development and documentation.
- Strong manufacturing network and capabilities: The global aseptic filling network is impressive, with a first-pass success rate as high as 94%. There are multiple factories located in the US, UK, Italy, Singapore, and other places, capable of producing various sterile preparations. The large molecule global network is also strong, with multiple bulk drug substance factories and rich experience in mammalian cell culture, technology transfer, and process development, providing end-to-end solutions from drug development to patient use.