The "White Paper on Chinese Medical Devices Going Overseas to Southeast Asia" mainly introduces the relevant situation of Chinese medical devices going overseas to Southeast Asia, including industry development, export trends, macro situation of Southeast Asian countries, opportunities in the medical industry and medical device industry, registration regulatory framework, overseas paths and regulations of various countries, aiming to provide reference for Chinese medical device companies going abroad.
1. Development of China's Medical Device Industry and Export Trends
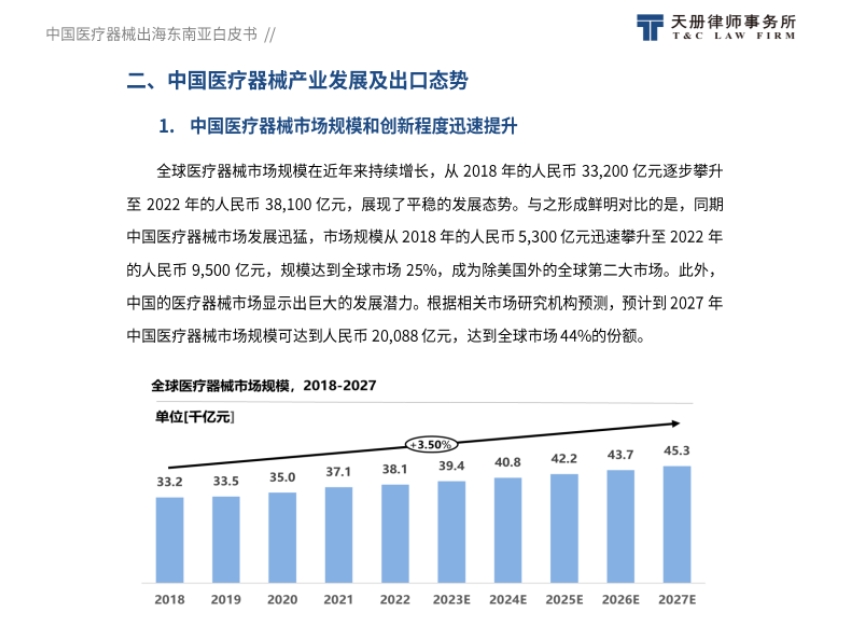
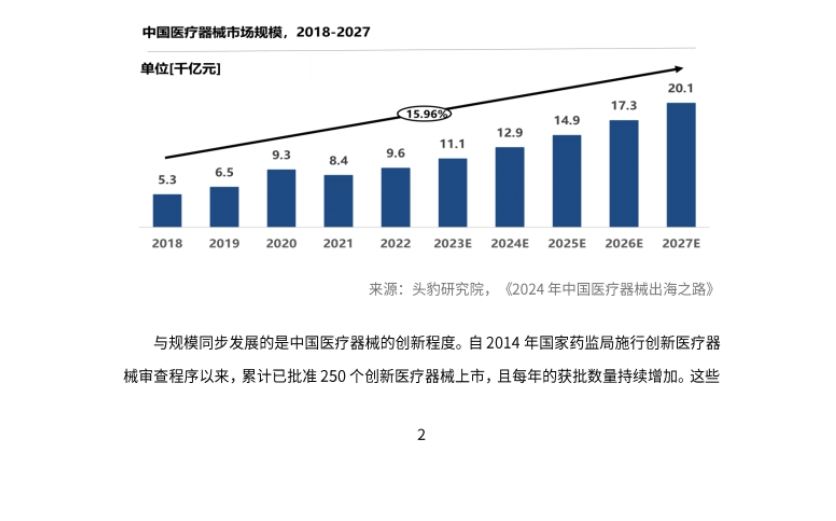
- Market Scale and Innovation Enhancement: The global medical device market size is steadily growing, and the Chinese market is developing rapidly, accounting for 25% of the global market, and is expected to reach 44% by 2027. China's medical device innovation capability continues to break through, with a total of 250 innovative medical devices approved for market since 2014, and domestic products accounting for 77%.
- Overall Export Situation: The export demand for Chinese medical devices is extensive, and export value grew rapidly during the COVID-19 pandemic, with product categories gradually diversifying and overseas competitiveness improving. The proportion of overseas revenue of A-share listed medical device companies increased from 24% in 2017 to 38.8% in 2021, and fell back to 34.9% in 2022. Low-value consumables remain the core export category.
- Export Situation to ASEAN Countries: ASEAN is the third largest export market for China's pharmaceutical and health products, and Chinese medical devices account for a large proportion of exports to ASEAN. In 2022, the export value to ASEAN was USD 13.68 billion, USD 11.3 billion in 2023, and USD 5.869 billion in the first half of 2024, a year-on-year increase of 2.64%. Among them, the export value of medical devices was USD 2.628 billion, a year-on-year increase of 1.12%. Vietnam, Thailand and other countries lead in export share in the ASEAN market.
2. Macro Introduction of Major Southeast Asian Countries and Analysis of Medical Industry Opportunities
- Overall Macro Situation
- Economic Scale and Per Capita GDP Growth: Southeast Asian countries have rapid economic growth and good post-pandemic recovery, with GDP growth rates exceeding China. In 2022, the total GDP reached USD 3.6 trillion, and is expected to reach USD 5.5 trillion by 2028. Per capita GDP reached USD 5,500 in 2022.
- Population and Structural Characteristics: Large population base, expanding middle class, young population structure but accelerating aging. In 2022, the total population reached 680 million, with some countries facing intensified aging issues, and healthcare demand will increase.
- Medical Expenditure Situation: Per capita medical expenditure and proportion of GDP are increasing, but there is still room for growth compared to developed countries. The compound annual growth rate of per capita medical expenditure from 2000 to 2019 was 9%.
- Opportunities for China's Medical Device Industry Going Overseas
- Government Emphasis on Medical Investment: Southeast Asian governments have focused on building the medical industry after the pandemic. For example, Malaysia's Ministry of Health budget has increased, and countries are focusing on hospital informatization, telemedicine, and medical tourism development.
- Dependence on Imported Medical Products: Southeast Asia's local medical product manufacturing industry is weak, and most medical devices rely on imports. Countries such as Singapore and Malaysia have high import ratios.
- Favorable Economic and Trade Cooperation Policies: China-ASEAN economic and trade cooperation is deepening, with a good policy environment. For example, the construction of free trade zones is advancing, the implementation of RCEP reduces policy risks, and both sides are cooperating in multiple fields.
3. Introduction to the Medical Industry and Medical Device Industry in Major Southeast Asian Countries
- Overview: PwC divides the medical markets of Southeast Asian countries into primary, emerging, and mature markets, each with different characteristics. Fitch Ratings predicts the compound annual growth rate of medical device markets in various countries, such as Indonesia at 10.8% and Vietnam at 10.2%.
- Discussion by Country
- Singapore: High medical expenditure, high service quality, severe population aging, and growing demand for telemedicine and home care. The medical device industry is developing rapidly, with a high dependence on imports, over 80% of demand relies on imports, and future imports are expected to grow by about 7.0%.
- Malaysia: Rich supply system for medical services, focus on prevention of non-communicable diseases and elderly care, many clinical research opportunities. There are many medical device manufacturers, leading in low-end product exports, while high-end equipment relies on imports, with an import ratio of 88%.
- Thailand: Developed medical tourism, aging population, growing demand for high-tech medical equipment. The medical device market is large but has a low self-sufficiency rate, with 90% relying on imports, and Chinese equipment accounts for the highest proportion of total imports.
- Indonesia: The government attaches importance to medical construction, integration of state-owned hospitals, aging population, facing a crisis of non-communicable diseases. The medical device market is growing rapidly, with a compound annual growth rate of 10.8% from 2021 to 2026, but government protectionist policies affect imports.
- Vietnam: Medical system transformation, increased expenditure, aging population, public and private hospitals face challenges, encouraging the import of medical equipment, with low tariffs and no quota restrictions. More than 90% of medical devices rely on imports, with an annual growth rate of 9.7% from 2021 to 2026.
- Philippines: The healthcare system consists of public and private sectors, universal health insurance coverage, emerging medical tourism, many opportunities in health IT and innovative medical device markets. Medical devices are highly dependent on imports, local production is limited to basic equipment and disposable products, and imports account for 99.2%.
4. Regulatory Framework and Overview of Medical Device Registration in Southeast Asian Countries
- Introduction to ASEAN Medical Device Directive (AMDD): AMDD was implemented in 2015 to harmonize regulatory standards, including basic principles, medical device technical documentation, classification, etc., to improve consistency in registration and regulatory standards.
- Overview of Medical Device Registration Regulation in Major Southeast Asian Countries: Countries differ in medical device classification, application materials, registration timelines, etc. The report introduces the basic registration requirements of major countries, and takes Singapore as an example to introduce registration paths, applicable requirements, and timelines in detail.
- Pre-registration Requirements and Timetables for Medical Devices in Major Southeast Asian Countries: Includes information on timelines, whether original country registration is required, reference countries, ISO 13485 certification requirements, etc. for Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand, and other countries.
- Singapore's Regulatory Registration Paths and Applicable Standards: Such as full path, immediate review, accelerated path, simplified path, etc., as well as applicable situations and application methods for priority approval.
- Introduction to Singapore's SAR Path for Importing Unregistered Medical Devices: Under specific circumstances, unregistered medical devices can be imported with separate approval without routine full registration.
- Singapore LDT Regulatory Framework and Requirements: LDT does not require review and registration, but clinical laboratories need to declare, maintain documentation, and comply with production control and post-market regulatory requirements.
- Thailand and Singapore's Reference Path: Thailand FDA recognizes Singapore HSA as a reference agency, which can accelerate the medical device registration process, and both parties need to submit documents as required.
5. Paths for Chinese Medical Devices Going Overseas to Southeast Asia and Introduction to Regulations in Various Countries
- Overseas Paths
- Distributor Model: Most companies adopt this in the initial stage, entering overseas markets through distributor networks, but need to select distributors carefully and manage cooperation risks.
- Local Assembly/Branding Model: Suitable for meeting specific country requirements, partner needs, or the company's own brand planning, but faces challenges in supply chain integration and intellectual property protection.
- Local Factory Establishment or Acquisition of Local Enterprises Model: Companies with large scale and a desire to deeply cultivate the local market can choose this, which allows management of supply chain and sales channels, but investment risks and management costs need to be considered.
- Regulations of Various Countries
- Indonesia: Product registration requires a designated local importer/distributor to apply for a circulation permit, and some medical devices require halal certification; distributors must comply with relevant regulations; there are localization production requirements and methods for calculating the domestic production rate; the medical device manufacturing and distribution sector is fully open to foreign investment, but certain conditions must be met.
- Vietnam: Sales of imported medical devices must meet circulation conditions, and registration requirements differ for different categories of medical devices; distributors are regulated for the sale of some medical devices; public hospitals are encouraged to use locally produced medical devices, and the domestic production rate can be judged with reference to the definition of the origin of goods; foreign investment has various forms, each with corresponding regulations.
- Singapore: Import of medical devices requires approval, and manufacturers and importers must assume corresponding responsibilities; local production and assembly can be carried out through cooperation with local partners, agreements must be signed and certification standards understood; there are no restrictions on foreign investment in medical device manufacturing and distribution enterprises, but certain conditions must be met.