This report mainly explores the background opportunities, current insights, challenges faced, and trend forecasts regarding the overseas expansion of Chinese cultural tourism enterprises and hotel brands, aiming to provide comprehensive market analysis and strategic guidance for relevant companies.
1. Background Opportunities
- Macroeconomic policy support: Policies such as the "Belt and Road" Initiative, the "Going Global" strategy, and the construction of a strong tourism nation provide support for cultural tourism enterprises to expand overseas, such as promoting tourism development, improving "Going Global" mechanisms, and encouraging enterprises to internationalize their layouts.
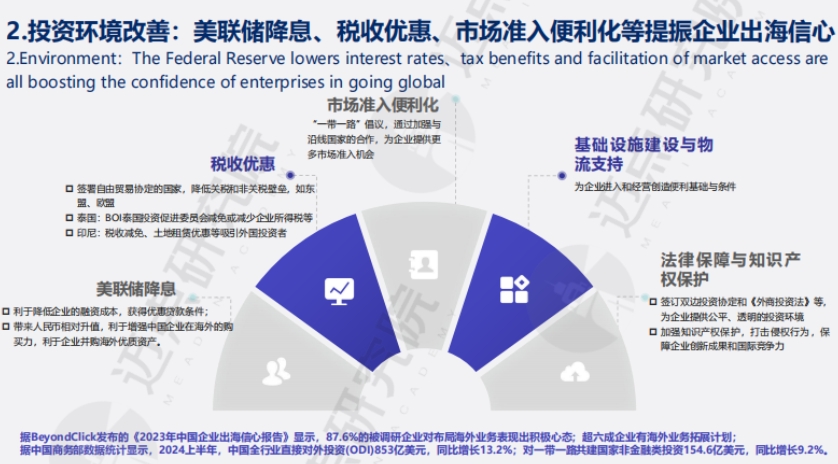
- Improved investment environment: The Federal Reserve's interest rate cuts, tax incentives, and market access facilitation have boosted companies' confidence in going abroad, including lowering financing costs, enhancing purchasing power, and providing legal protection. Enterprises are highly motivated to go overseas, and outbound investment is growing.
- Outbound tourism market drive: The global travel market is recovering, Chinese outbound tourism is gradually resuming, and in 2024 international inbound and outbound tourism will fully recover. The number of Chinese outbound tourists is expected to increase, which will drive cultural tourism enterprises to go abroad.
- Industry strength enhancement: The influence of Chinese cultural tourism enterprises is expanding, and domestic hotel group brands are rising, performing well in global theme park operator and hotel group rankings.
2. Current Insights
- Overseas expansion models and paths of cultural tourism enterprises
- Online travel service providers: Such as Ctrip, Fliggy, Tongcheng Travel, Meituan, etc., accelerate global layout and cooperation by leveraging their respective advantages, mainly through overseas acquisitions and strategic cooperation, covering areas such as visas, SIM cards, travel and entertainment, with a wide range of overseas regions.
- Theme park operators: Early starters in overseas expansion, mainly adopting light asset output models, such as Huaqiang Fantawild, Hong Kong CTS - Splendid China, etc. Some companies also have heavy asset investment models, with varying progress.
- Comprehensive cultural tourism groups: Strong capabilities, wide global layout, and diversified overseas expansion models, such as China Travel Group, Club Med, Wanda Group, OCT Group, Fosun International, etc., expanding overseas markets through various businesses.
- Overseas expansion history and models of hotel brands
- Expansion history: Four stages including initial attempts, buying buildings to operate hotels, mergers and acquisitions for expansion, and deepening layout, continuously exploring internationalization paths. Representative acquisition events at different stages by companies such as Jinjiang and Huazhu.
- Expansion models: The first round was developer-led, adopting a heavy asset model, mainly targeting developed countries; the second round was hotel group-led, favoring light asset models, with destinations shifting to Southeast Asia and emerging markets along the "Belt and Road", involving the overseas output of many hotel groups and brands.
3. Overseas Challenges
- Multiple challenge factors: Facing challenges such as international brand competition, cultural differences, changes in policies and regulations, market access barriers, technological adaptability, supply chain management, economic fluctuations, international relations, and labor systems, which affect the process of overseas expansion.
- Case insights
- Disney Park case: Paris Disneyland suffered losses due to cultural differences, misjudgment of consumer habits, and operational management issues; Tokyo DisneySea's opening was delayed due to project shelving, extended construction periods, and logistics restrictions, indicating that overseas cultural tourism projects are affected by various uncertainties.
- Overseas hotel acquisition cases: Cultural tourism real estate companies such as Wanda and Greenland sold overseas assets due to funding issues; Jinjiang's acquisition of Louvre Hotels Group and Huazhu's acquisition of Deutsche Hospitality faced operational challenges such as net profit losses, indicating difficulties in sustained operation and rooting after overseas acquisitions.
4. Trend Forecasts
- Overseas expansion is an inevitable trend: "Go overseas or be eliminated" has become a consensus. Enterprises have the capability to go abroad, driven by global capital flows, external market attraction, favorable policies, and internal development needs, accelerating the process of going overseas.
- Overseas strategy recommendations: Favor light asset models, rely on the Chinese outbound tourism market, select high-quality partners, conduct thorough market research and localization/compliance management, strengthen brand building and enhancement to cope with risks and improve competitiveness.
- Regional selection for overseas expansion: Focus on expanding into emerging markets along the "Belt and Road" such as East Asia, Southeast Asia, the Middle East, and Africa, while also competing for opportunity markets in Europe and America, based on factors such as culture, market demand, policy, and cost.
- Outlook and significance of going overseas: Overseas expansion will provide momentum for the global tourism industry. Enterprises should flexibly choose overseas expansion methods according to their own situations, balance long-term strategies with short-term goals, and contribute to cultural export and the enhancement of international influence.